10 interesting facts about cells: The building blocks of life
The basic unit of life is called a cell. All single-cell or multi-cell life forms composed of cells and their existence depend on the normal function of the cells. There are hundreds of different forms of cells in organisms, and it is estimated that there are between 75 and 100 trillion cells in an adult. Cells provide stability and structure to the body, produce energy and reproduce. In the next section, 10 interesting facts about cells are stated:
1. Cells are too small:
The cell size varies from 1 to 100 µm. Without the appearance of the microscope, cell research, namely cell biology, would not be possible. Using modern microscopes, such as transmission electron microscopes and scanning electron microscopes, cell biologists can obtain better images of the smallest cell structures.
2. Two main types of cells:
The two main types of cells are called prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. The nucleus of prokaryotes is not enclosed in a membrane; for example: bacteria and archaea. Eukaryotic cells have a real nucleus, wrapped in a membrane; for example: plants, animals, protists and fungi.
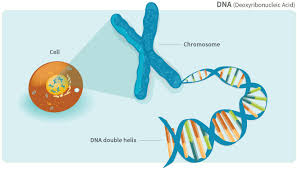
3. All cells have genetic material:
RNA (ribonucleic acid) and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) are found in cells that have the genetic information needed to regulate different cells.
4. Cells have organelles:
Organelles have many different functions within the cell, covering everything from energy supply to the production of hormones and enzymes. Eukaryotic cells contain many types of organelles, while prokaryotic cells contain fewer organelles. There are also some differences between the types of organelles found in different eukaryotic cells. Some important organelles are ribosomes, mitochondria, nuclei, and Golgi complexes.
5. The primitive form of life is the cell:
Prokaryotic cells are considered the primitive form of life because they can live in areas that may be harmful to other organisms. These extreme microorganisms can survive and multiply in various extreme environments. For example, archaea live in animal intestines, swamps, hot springs, and hydrothermal vents.
6. A group of identical cells form a tissue:
The same cell group that has a common function and structure is called a tissue. The cells that form animal tissues are bound together with the extracellular fibers of the cells, sometimes by a sticky substance covering the cells. Different types of tissues can also be combined to form organs.
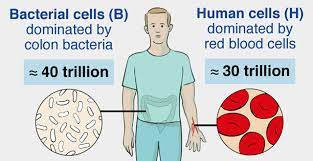
7. There are fewer human cells than bacterial cells in the human body:
It is estimated that approximately 95% of all cells in the human body are bacterial cells. Most of these bacteria can exist on the digestive tract and skin.
8. Cells have different life cycles:
Cells in the human body have different lifespans, depending on the function and type of the cell. They can live from a few days to a year. Some digestive cells can only survive for a few days, while immune system cells can survive for up to six weeks. Pancreatic cells can survive for up to a year.
9. Cells have different ways of reproduction:
Many prokaryotic cells replicate themselves through a process called binary fission. Eukaryotes can also reproduce through mitosis. In addition, some eukaryotes can reproduce themselves through sex. This involves the synthesis of sex cells or gametes, which are produced through a process called meiosis.
10. Cell suicide:
If a cell is damaged or infected, it will destroy itself through a process called apoptosis. The role of apoptosis is to ensure the normal development and maintenance of the mitotic natural immune system. The inability of cells to detect apoptosis can lead to the development of cancer.
Related Posts
- Emerging Sustainable Tech Innovations Shaping a More Environmentally Friendly Future
- How to adjust smartphone settings
- 5 Solutions for Video Streaming Issues on Various Devices
- 10 Must-Have Smart Home Devices for 2024
- How to protect your device from malware
- The Impact of Artificial Intelligence in the Healthcare Sector